Micro switches, those small, pivotal components found in many electronic devices, might not dominate headlines, but their importance cannot be overstated. Whether you're an electronics enthusiast, a DIYer, or a tech hobbyist, understanding micro switches can significantly boost your projects. Here's a comprehensive guide to the ten most crucial aspects of micro switches you should be familiar with.
If you're working on a project using micro switches, our website offers a wide range of micro switch products, and we can also produce customized micro switches based on your requirements. OpenELAB is a one-stop development platform for global AIoT electronics enthusiasts and an open-source community for electronic engineers. Besides providing developer modules online, our services also include customized manufacturing of various electronic parts such as micro switches and batteries, as well as plastic or metal parts through 3D printing, injection molding, CNC, laser cutting etc.
What Is a Micro Switch?
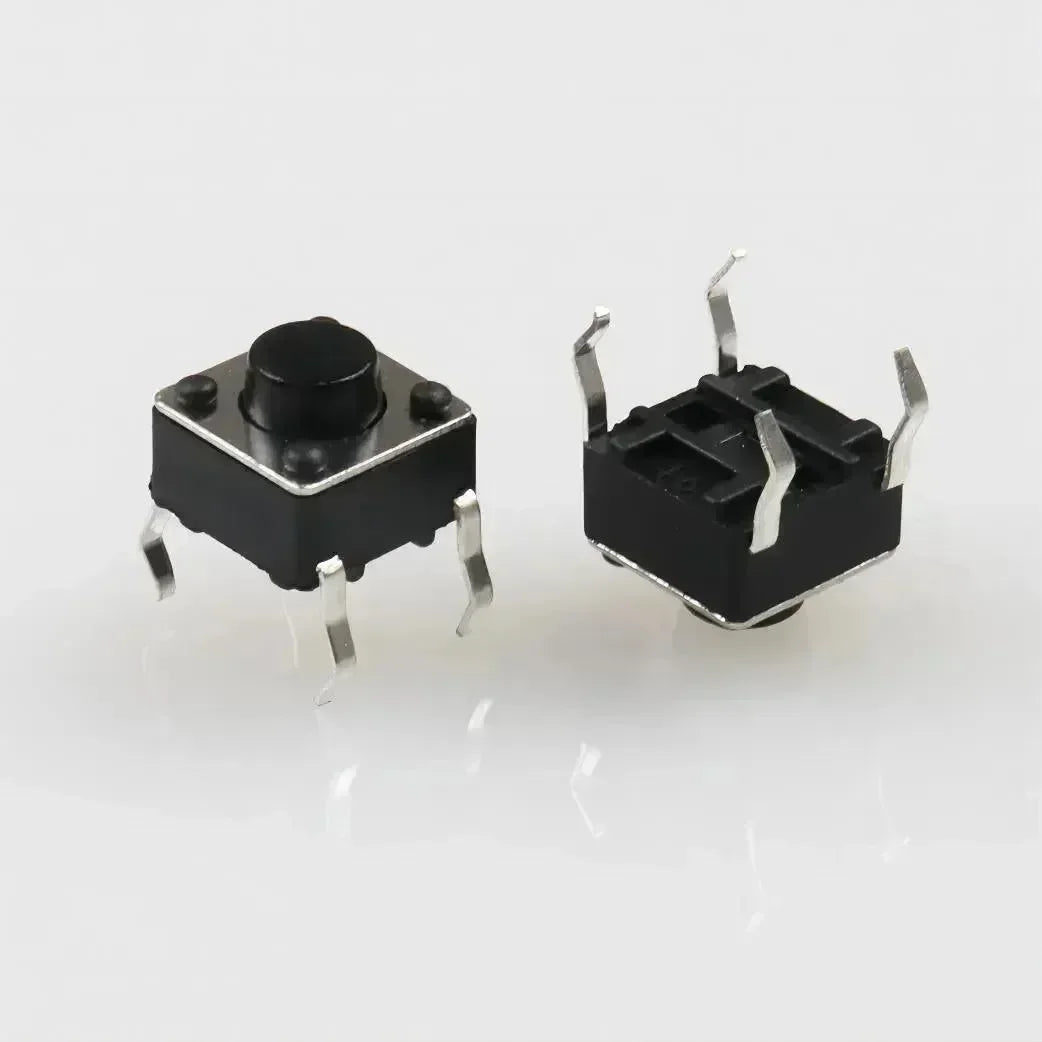
The micro-switch is a switch that operates rapidly with a very small amount of force. The micro-switch is also called a miniature snap-action switch. It is extremely reliable, fast, and efficient to operate and is also known as a miniature snap-action switch. It is impossible to create smart appliances without microswitches. They are used in many modern-day smart applications. Microswitches are often used as safety devices because of their reliability and sensitivity. They are used to prevent the closing of doors when something or someone is in the way and other similar applications.
The micro switch has three pins: Common (C), Normally Closing (NC), and Normally Opening (NO). Here, the Common pin is an input pin, the NC pin is Output 1, and the NO pin is Output 2.
With its tiny contact gap, The micro switch is a snap-action precision switch for logic-level and power-duty loads. The switch has options like SPDT, SPNO, or SPNC, and offers power-duty switching through silver alloy contacts. Different electrical terminations are available, and logic-level control can be achieved by silver alloy or gold-plated contacts.
How Does a Micro Switch Work?
A micro switch is a highly responsive device equipped with an actuator that manipulates a lever to alter the contact configuration when pressed. This action is usually accompanied by a distinctive “clicking” sound, signaling that the switch has been activated. Micro switches are designed with mounting holes, allowing for easy and secure installation in various applications. Their simplicity ensures minimal maintenance and a long lifespan, rarely necessitating replacement.
Operating Principle of a Micro Switch
The core functionality of a micro switch lies in its ability to quickly change the state of electrical contacts. Upon pressing the lever, the normally closed (NC) contact opens, and the normally open (NO) contact closes. Releasing the lever reverses this action, where the NC contact resumes carrying current, and the NO contact remains electrically isolated.
A critical feature of the micro switch is its tipping-point mechanism. This mechanism is crucial for establishing precise tripping and resetting points where the contacts will change state. This ensures reliable operation across countless cycles, making the micro switch an integral component in both simple and complex devices.
What Is the Structure of a Microswitch?
The structure of a microswitch includes a housing, an actuator, a set of contacts (NO, NC, and C), a terminal, and a spring. The housing is usually made from durable materials like plastic or metal to protect the internal components. The actuator mechanism is what triggers the switch's operation, influenced by the movement of the spring-loaded lever.

Plunger or Actuator
The plunger or actuator is the part of the microswitch that experiences external force. This component is what initiates the switch's operation. Depending on the design, plungers can vary in shape and size, tailored to specific applications. From button types to roller designs, each serves the purpose of translating physical pressure into electrical action.
Cover
The cover of a microswitch is designed to protect its internal components from dust, moisture, and external contaminants. This protective casing is crucial in maintaining the switch's reliability and longevity, especially in harsh environments.
Moving Piece
Inside the microswitch, the moving piece, often linked to the actuator, is responsible for the switch's action. This component moves in response to external force, making or breaking the electrical connection.
Support
The support structure within a microswitch holds all the components in place, ensuring that the moving piece can operate smoothly and precisely. This base is the backbone of the switch, providing stability and alignment for accurate functionality.
NC Terminal
The Normally Closed (NC) terminal is one of the switch's contact points. In its default state, the circuit between the NC terminal and the common terminal is complete, allowing current to flow. When the switch is activated, this connection is broken.
NO Terminal
Conversely, the Normally Open (NO) terminal is disconnected in the switch's default state. It only establishes a circuit with the common terminal when the switch is actuated, allowing current to pass through.
Contact
The contact is where the electrical connection is made or broken within the switch. High-quality materials, such as gold or silver alloys, are often used for contacts to ensure reliable conductivity and resistance to corrosion.
Moving Arm
The moving arm connects the moving piece to the contact. It translates the motion of the actuator into the opening or closing of the electrical circuit. The precision of the moving arm's operation is vital for the accurate performance of the microswitch.
The structure of a microswitch might appear simple at first glance, but its design is the result of sophisticated engineering. Each component plays a critical role in delivering the switch's fast and reliable performance.
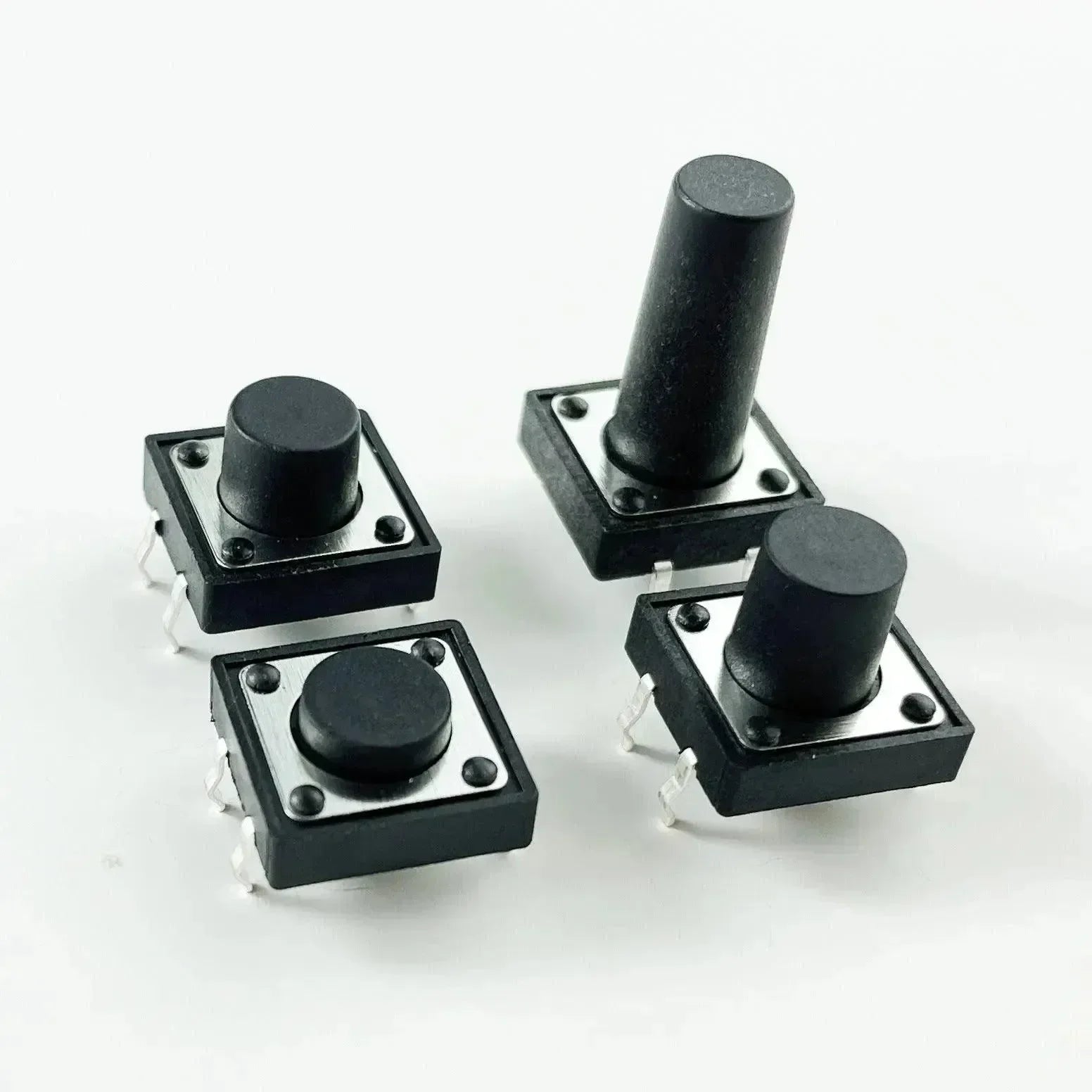
Different Types of Micro Switches
There are several types of micro switches, including standard, sub-miniature, and miniature. They can also vary by actuator type, such as lever, push-button, or roller designs. Each type has its unique advantages and suitable applications. We’ll discuss some types of micro switches in the below.
Standard Micro Switches
These are the typical, widely used micro switches with standard dimensions. They are robust and versatile, used in various applications where space is not a major constraint. They can handle higher current loads compared to smaller versions, making them suitable for industrial equipment, automotive applications, and home appliances.

Sub-miniature Micro Switches
Sub-miniature micro switches are smaller than standard switches but still offer excellent durability and reliability. They are ideal for applications where space is limited but where a high level of performance is necessary. Typical uses include in medical devices, mobile phones, and other portable electronics where compactness is essential.

Miniature Micro Switches
Even smaller than sub-miniature types, miniature micro switches are used in extremely space-constrained environments. Despite their small size, they maintain high reliability and precision. Common applications include small household appliances, office equipment, and compact electronic devices.

Lever Actuated Micro Switches
Lever actuated micro switches incorporate a lever as a part of the actuator mechanism. The lever amplifies the actuation force, allowing for easier operation and enabling the switch to be triggered by less direct actions, such as the movement of a machine part or door. They are commonly used in industrial controls, vending machines, and safety equipment.

Push-Button Micro Switches
These switches are activated by a push-button actuator. They are straightforward to use and are commonly found in consumer electronics and machinery as start or stop buttons. Push-button micro switches are also often used in emergency equipment, where a quick and easy method of activation is crucial.
Roller Design Micro Switches
Roller design micro switches feature a roller at the end of the lever. This design minimizes wear and tear on the actuator itself and allows for smooth, consistent actuation as objects pass over the roller. They are ideal for use in applications where a moving object activates the switch, such as in conveyor systems or in door mechanisms.

Sealed Micro Switches
Sealed micro switches are designed to withstand harsh environments where exposure to dust, moisture, or corrosive elements is common. These switches are typically encapsulated or have tightly sealed housings to prevent the ingress of damaging substances. They are used extensively in outdoor, automotive, or industrial applications where such exposures are unavoidable.

Each type of micro switch is tailored to specific operational needs and environmental conditions, making them a versatile choice for many electrical and mechanical applications. Whether in consumer electronics, industrial machinery, or vehicles, there's a micro switch type suitable for virtually any setting.
The differences between Micro Switch and Limit Switch
In the world of electronics and engineering, the subtle differences between components can lead to significant improvements in the design and functionality of a project. Two commonly confused elements are micro switches and limit switches.
The below form aims to demystify these components for engineers, tech enthusiasts, DIYers, and tech hobbyists, highlighting their differences in size, cycle index, usage scenarios, methods of application, types, and response time.

How To Maintain a Micro Switch for Longevity and Reliability
Follow a comprehensive guide on keeping your micro switches in top condition, ensuring their longevity and reliability:
Keep It Clean
One of the most fundamental yet often overlooked aspects of micro switch maintenance is cleanliness. Dust, debris, and other contaminants can accumulate over time, potentially obstructing the switch's actuator mechanism or compromising the electrical contacts. Here's how you can keep your micro switches clean:
-
Use Compressed Air: A blast of compressed air can effectively remove loose dust and debris from the switch housing.
-
Apply Electrical Contact Cleaner: For more thorough cleaning, use an electrical contact cleaner spray. It’s designed to dissolve and remove greasy buildups without leaving residue or damaging the components.
Avoid harsh environments
Micro switches are generally durable, but prolonged exposure to harsh environments can shorten their lifespan. Moisture, extreme temperatures, and corrosive chemicals are some conditions to avoid:
-
Moisture Protection: Keep micro switches away from wet environments. If exposure to moisture is unavoidable, consider using switches with higher IP ratings (Ingress Protection) designed for such conditions.
-
Temperature Control: Extreme heat or cold can affect the physical and electrical properties of micro switches. Use switches rated for your project's specific temperature range.
-
Chemical Resistance: In environments where exposure to chemicals is possible, opt for micro switches made with materials resistant to corrosion.
Inspect Contact Parts
The contact points inside a micro switch are critical for its operation. Over time, these contacts can wear out or become oxidized, leading to poor conductivity and switch failure:
-
Visual Inspection: Regularly inspect the contact points for signs of wear or oxidation. A magnifying glass can help in spotting these issues.
-
Clean Contacts: If oxidation is present, carefully clean the contacts with a contact cleaner or a gentle abrasive like a pencil eraser.
Monitor voltage and current
Exceeding a micro switch’s rated voltage or current can cause premature failure due to excessive heat or arcing at the contacts:
-
Stay Within Specifications: Always adhere to the voltage and current ratings specified by the micro switch manufacturer.
-
Use Protective Circuitry: Incorporating protective elements like fuses or current limiters can help prevent accidental overloads.
Periodic maintenance
Regular, periodic maintenance can significantly extend the life of a micro switch:
-
Schedule Inspections: Establish a routine schedule to inspect, clean, and test your micro switches. The frequency will depend on the switch's usage and environmental conditions.
-
Test Functionality: Use a multimeter to check the continuity of the switch in its open and closed states. This can help identify any potential issues before they lead to failure.
By following these maintenance tips, you can ensure that your micro switches will perform reliably for years to come. Remember, the key to longevity in electronics is not just in choosing high-quality components but also in maintaining them with care and precision. Whether you're working on a personal project or professional equipment, a little maintenance goes a long way in preserving the functionality and reliability of your devices.
Advantages & Disadvantages of micro switches
Advantages:
High Reliability
One of the most significant advantages of micro switches is their reliability. They are designed to work in various conditions and can endure millions of cycles before failing. This high reliability makes them ideal for safety mechanisms in equipment where failure could result in significant damage or danger.
Precise Operation
Micro switches are known for their precision. They operate at specific and repeatable positions, providing accurate and consistent results. This precision ensures that devices function correctly every time, an essential factor in applications requiring exact control.
Cost-Effectiveness
Despite their high reliability and precision, micro switches are relatively inexpensive. Their low cost makes them an attractive option for manufacturers looking to keep production costs down without compromising on quality.
Versatility
The versatility of micro switches is evident in their wide range of applications. They can be found in consumer electronics, automotive industry, medical devices, and even aerospace technology. This adaptability stems from their variety in sizes, actuator styles, and switching capacities.
Fast Response Time
Micro switches respond quickly to changes, making them suitable for applications that require rapid switching. Their snap-action mechanism ensures that the switch operates swiftly, reducing the time it takes for a device to respond to user inputs or environmental changes.
Disadvantages:
Limited Power Handling
One drawback of micro switches is their limited power handling capabilities. While perfect for low-power applications, they might not be suitable for high-power tasks without additional relays or power management devices. This limitation can restrict their use in certain industrial applications.
Environmental Sensitivity
Although micro switches are designed to be durable, they can be sensitive to extreme environmental conditions such as high humidity, temperature fluctuations, and corrosive atmospheres. These conditions can affect their performance and longevity, necessitating careful consideration of the operating environment.
Mechanical Wear and Tear
Like any mechanical device, micro switches are subject to wear and tear over time. The repeated actuation can lead to material fatigue, potentially affecting the switch's reliability and lifespan. Regular maintenance and replacement are essential to ensure continued performance.
Installation and Positioning Challenges
The effectiveness of a micro switch heavily relies on its correct installation and positioning. Improper alignment can lead to premature failure or inaccurate operation, requiring precision during the setup phase. This aspect can pose challenges, especially in complex systems or confined spaces.
Noise
The snap-action mechanism of micro switches can generate noise during operation. While this may not be a concern in industrial environments, it could be undesirable in consumer applications where noise is a significant consideration.
Understanding these pros and cons ensures that you can leverage the advantages of micro switches while mitigating their drawbacks, leading to successful and efficient project outcomes.
Micro Swicth Applications
Micro switches are versatile and found in a wide range of applications. Here are a few examples:
Home Appliances: Washing machines, refrigerators, and air conditioners use micro switches to detect doors or lids' closure and control various functions.
Industrial Controls: In industrial settings, micro switches are key components in control systems for machinery, ensuring safety and functionality.
Automotive: Vehicles utilize micro switches for various controls, including turn signals, power windows, and door locks, enhancing both convenience and safety.
Consumer Electronics: Gadgets and devices often incorporate micro switches for buttons and other interactive components, providing tactile feedback to users.
Understanding these applications and how micro switches function within them can help you recognize their critical role in everyday technology and select the appropriate switch for any project.
Final Words
Understanding the fundamentals of micro switches can enhance your electronics projects and help you make informed decisions when selecting components. Whether you're designing a new device or repairing an existing one, little knowledge about micro switches goes a long way. Remember to consider your project's specific needs and constraints when choosing a micro switch, and you'll be well on your way to achieving reliable and effective results.
If you're working on a project using micro switches, our website offers a wide range of micro switch products, and we can also produce customized micro switches based on your requirements.
OpenELAB is a one-stop development platform for global AIoT electronics enthusiasts and an open-source community for electronic engineers. Besides providing developer modules online, our services also include customized manufacturing of various electronic parts such as micro switches and batteries, as well as plastic or metal parts through 3D printing, injection molding, CNC, laser cutting etc.
In addition to micro switches,OpenELAB offers other electronic component sourcing services such as sensors, displays, IoT, and more.OpenELAB has a user-friendly website that makes it easy to find the components you need, and we offer fast shipping to customers around the world.
Moreover,OpenELAB offers Design as a Service (DaaS) for design optimization, Manufacturing as a Service (MaaS) for production manufacturing, Supply Chain as a Service (SaaS) for supply chain support, and Quality as a Service (QaaS) for quality control to AIoT products transitioning into mass production, ensuring a smooth transition to the commercial production phase.
Most importantly, OpenELAB is dedicated to building a global open-source community for AIoT electronic developers. Through the OpenELAB open community, developers in the AIoT electronic revolution can collaborate, empower each other, and create a culture of mutual respect and collaborative sharing, generating more innovative AIoT intelligent hardware products for the world.
 openelab.de
openelab.de
 openelab.com
openelab.com