As Boston Dynamics' Atlas masters complex acrobatics and Tesla's Optimus refines dexterous manipulation, humanoid robots are steadily transitioning from laboratory curiosities to tangible real-world assets. Yet, a fundamental challenge persists, separating these sophisticated machines from true autonomous intelligence: How can they, like or even beyond human capabilities, accurately "see," comprehend intricate 3D environments, decipher object semantics, and understand dynamic changes to facilitate precise physical interaction?

In an era where mobile intelligent robots are increasingly permeating industries from manufacturing to healthcare, advanced perception remains the linchpin of their autonomy and intelligence. The rise of embodied intelligence intensifies this need. Unlike virtual AI relying solely on cloud computing, embodied AI demands robots interact with the physical world in real-time, requiring them to evolve into physical AI. This necessitates perceiving millimeter-level displacements of dynamic obstacles, judging object texture and rigidity for grasping, and even interpreting subtle human gestures to accomplish tasks like navigation, obstacle avoidance, interaction, and grasping with unparalleled precision.
The Bottlenecks of Traditional Robot Vision Solutions
Historically, conventional vision technologies have struggled with inherent limitations, such as ambient light interference, insufficient ranging accuracy, and inefficient multi-sensor collaboration. These issues often hinder robots from achieving stable and efficient perception in complex, dynamic environments. Solutions attempting to fuse multiple independent sensors frequently result in overly complex, cumbersome, and difficult-to-deploy or mass-produce systems.

Let's delve into the persistent "shackles" of traditional approaches:
1. The Inherent Shortcomings of Passive Vision
Traditional structured light vision, reliant on ambient light for passive imaging, suffers significantly from varying lighting conditions. In overly bright or dim environments, crucial image information is often lost, preventing robots from accurately identifying object contours or distances. Consider traditional AGVs/AMRs that frequently halt due to visual failures when exposed to direct sunlight or alternating shadows. Similarly, a humanoid robot operating in a factory or home might face fast-moving obstacles (e.g., a pet or a falling tool). Due to low frame rates and high data processing latency, conventional structured light cameras struggle to update environmental models in real-time, leading to delayed robot responses or even collisions.
2. Accuracy Woes of Binocular and Structured Light
While binocular cameras can calculate depth via parallax, their ranging accuracy deteriorates sharply with distance, and their resistance to ambient light is weak. Structured light offers high-precision close-range 3D reconstruction but is vulnerable to pattern interference, rendering it almost ineffective beyond 5 meters or in bright outdoor conditions. iToF technology provides fast ranging but is susceptible to multipath reflection, leading to noisy and less robust data. When a robotic arm needs to grasp a delicate egg or tighten a precision screw, the vision system demands sub-centimeter-level depth information. Yet, traditional solutions often experience significant accuracy drops in strong light and suffer from parallax errors at close range, culminating in high grasping failure rates.
3. The "Bloat Trap" of Multi-Sensor Stacking
To compensate for individual sensor limitations, some manufacturers combine cameras with LiDAR (dToF) for enhanced perception. However, this approach introduces complex hardware deployment, painstaking calibration, and substantial computing costs. Developers often dedicate months to achieving time synchronization, data alignment, and algorithm fusion, only to find the resulting system too complex for scalable implementation. The challenge is magnified with embodied intelligence, which requires fusing multi-dimensional data like vision, touch, and force feedback. The spatial-temporal misalignment of outputs from traditional cameras, LiDAR, and tactile sensors often forces developers into prolonged calibration efforts, still without guaranteeing perception in all complex scenarios.

These technical bottlenecks not only restrict a robot's adaptability but also impede industry innovation, forcing developers to build foundational toolchains rather than focusing on functional optimization and scenario expansion.
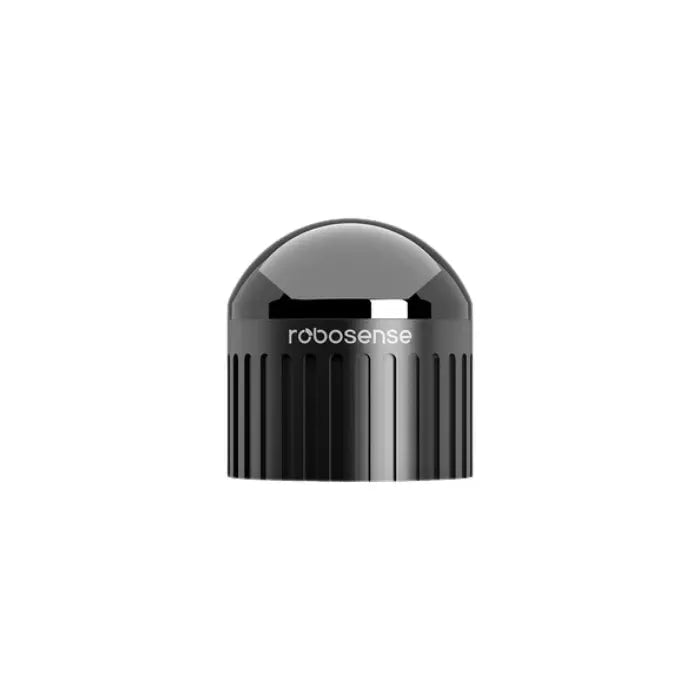
Introducing RoboSense AC1: A Disruptive One-Stop Solution for Robot Perception
On March 28, 2025, RoboSense unveiled its groundbreaking RoboSense AC1 LiDAR Depth Camera, the first product in its new Active Camera series, alongside an AI-Ready ecosystem. This innovative offering presents a disruptive, one-stop solution for robot perception development, directly addressing the core challenges highlighted above.

The AC1 provides hardware-level fused information of depth, color, and motion posture, fundamentally transforming robot perception configurations. It moves beyond the traditional, cumbersome method of stacking disparate sensors, evolving into a simple, efficient, and commercially viable solution for mass production. Simultaneously, the AI-Ready ecosystem equips developers with essential software tools and open-source algorithms, significantly improving development efficiency and shortening cycles. This powerful combination of hardware-level fusion and a comprehensive developer ecosystem is set to redefine robot vision, establishing a new paradigm for AI perception and ushering in an evolution for robots to possess truly discerning "eyes."

Key Features & Disruptive Breakthroughs of the RoboSense AC1:
The RoboSense AC1 isn't merely an upgrade; it's a qualitative leap in 3D perception, built on deep hardware-level innovation. Its core advantages revolve around ultra-precise ranging, unparalleled environmental robustness, and comprehensive all-scenario adaptability.
-
Hardware-Level Multi-Modal Fusion for Spatio-Temporal Unity:
The AC1 achieves true hardware-level fusion by deeply integrating the digital signals of LiDAR with camera visual information. Through RoboSense's self-developed chip-level algorithms, the AC1 outputs spatio-temporally synchronized depth information, color information (RGB), and motion posture information (IMU). This breakthrough eliminates the data asynchronous and accumulated calibration errors inherent in traditional multi-sensor setups. In dynamic obstacle avoidance, for instance, AC1 delivers high-precision point clouds and semantic images in real-time, enabling robots to simultaneously perceive an obstacle's position, shape, and motion trend. -
Industry-Leading Performance Metrics:
The AC1 surpasses human visual capabilities in several aspects:- Ultra-Precise Depth Sensing: Achieves an impressive 3cm (1σ) accuracy with a maximum range extended to 70 meters. This is a 600% increase in ranging capability compared to many traditional 3D cameras, providing pinpoint 3D spatial data crucial for advanced SLAM and autonomous navigation.
-
Expansive Field of View (FoV): Offers a wide Depth FOV of 120° × 60° and an RGB FOV of 144° × 78°, which is 170% larger than traditional 3D cameras. This expansive coverage ensures full-scene awareness and robust object tracking

-
Unrivaled Environmental Robustness:
Crucially, the AC1's ranging performance is impervious to lighting conditions. It operates reliably under 100kLux of direct sunlight and maintains consistent data quality even in no-light environments. This means robots can not only acquire precise 3D distance data but also rich visual semantic information, overcoming environmental interferences like strong light and darkness. For the first time, robots gain all-weather, all-terrain "visual freedom." -
Compact, Rugged & Cost-Effective Design:
Unlike multi-sensor stacking solutions that demand complex mechanical structures, the highly integrated AC1 is significantly more compact – roughly 1/3 the size of traditional multi-sensor setups. This lightweight, solid-state module is engineered to withstand extreme temperatures from -20°C to 60°C, making it ideal for flexible deployment on various mobile platforms like AGVs, drones, service robots, and humanoid robots. Furthermore, its single-device cost is 40% lower than a separate "camera + LiDAR" combination, paving the way for broad commercialization.
Li Yuexuan, an algorithm engineer at the National and Local Joint Engineering Research Center for Humanoid Robots, noted: "The space available for deploying sensors on existing humanoid robots is limited, separate sensor calibration is troublesome, and there's a lack of easy-to-use multi-sensor fusion algorithms. AC1 saves deployment space and can directly fuse image, point cloud, and IMU algorithms, achieving excellent SLAM, perception, and localization effects."
Yang Guodong, co-founder and head of the Motion Intelligence R&D Center at Lingbao CASBOT, added: "Our perception and hardware teams are very satisfied with AC1. It eliminates the tedious work of calibrating different sensors separately and reduces the number of hardware components, saving internal space, which is very friendly for the design of compact humanoid robots."

Empowering Developers: The AI-Ready Ecosystem Unlocks Innovation
The technological prowess of AC1 is only part of its value; RoboSense's deeper strategy lies in cultivating a developer-friendly ecosystem that is poised to revolutionize the robotics industry's development paradigm.
Traditionally, developers spend up to 80% of their effort on foundational tasks like sensor driver development, data calibration, and time synchronization. AC1's AI-Ready ecosystem provides a comprehensive open-source toolkit, including drivers, data collection nodes, calibration tools, multi-modal data fusion interfaces, and even a pre-configured cross-compilation environment. This allows developers to transition from "reinventing the wheel" to rapidly "building with blocks," shortening development cycles from months to mere weeks.

For example, for SLAM and localization modules, AC1 supports visual-LiDAR fusion SLAM, enabling high-precision localization in dynamic environments. It also facilitates 3D Gaussian Splatting, helping developers achieve efficient reconstruction of sparse point clouds more quickly while reducing computing power consumption. Furthermore, AC1 includes semantic segmentation and object recognition function modules, empowering developers to quickly achieve real-time recognition of dozens of object types (e.g., industrial parts, pedestrians, vehicles) based on pre-trained models.
The feature-rich SDK for the Active Camera series allows developers to meet diverse scenario-specific tasks. Leveraging AC1's automatic association of point cloud and visual data, its multi-modal fusion capabilities significantly enhance scene understanding. Developers can directly access functions like SLAM mapping, 3D Gaussian, localization, and obstacle avoidance via the SDK, bypassing tedious sensor driver development, calibration, and data fusion. They can tune existing algorithms for specific scenarios, or quickly integrate advanced functions such as semantic segmentation, object recognition, and path planning through intuitive APIs, without needing to train models from scratch.
To cater to varied industry needs, the Active Camera product line will expand, offering different types of products to meet specific requirements for ranging, accuracy, resolution, and ambient light resistance. Developers can choose resolution, ranging capabilities, and power consumption levels based on their task. For instance, logistics robots might prioritize a large field of view and anti-interference mode, while medical robots could opt for high-precision mode for critical obstacle avoidance. This flexibility ensures the Active Camera covers a full spectrum of applications, from industrial inspection to home services, optimizing sensor principles for various scenarios.
RoboSense is actively collaborating with numerous developer communities and university labs worldwide to continuously enhance its algorithm library and toolchain. Complementing this, technical support centers in the United States, Europe, and the Asia-Pacific ensure global developers have seamless access to the ecosystem and support.
Conclusion: Redefining Robot Vision with RoboSense AC1
As a globally leading robotics technology platform, RoboSense, through its AC1 LiDAR Depth Camera and AI-Ready ecosystem, is poised to become the definitive "perception standard-setter" for the intelligent robotics industry.
Unlike traditional component suppliers offering isolated modules (cameras, radars, IMUs), RoboSense provides a holistic, closed-loop fusion solution from hardware to algorithms, embodying a "perception-decision-execution" philosophy. This significantly lowers the R&D barrier for robot developers.
Leveraging RoboSense's extensive technological accumulation and industrialization capabilities, the AC1 boasts both high cost-effectiveness and ease of use. This democratizes advanced perception, enabling even small and medium-sized enterprises and startups to rapidly develop robot products with cutting-edge capabilities. This acceleration promises to expand intelligent robots into diverse "long-tail" scenarios, such as agriculture, construction, and retail.

The advent of AC1 marks a pivotal transition for robot vision – from "passive imaging" to "active perception." It's not just a superior replacement for traditional 3D cameras; it resolves the application limitations and compatibility issues of multi-vision sensor stacking. The AC1 embodies a new technological philosophy: through deep integration of hardware and algorithms, it empowers robot perception to genuinely transcend human sensory limitations, propelling us towards spatial intelligence.

For engineers and developers, AC1's AI-Ready ecosystem transforms them from mere "tool users" into "innovation leaders." For the industry, this represents an efficiency revolution and, more importantly, the dawn of the next evolution of intelligent robots.
As the Active Camera product line expands, RoboSense will continue to drive the evolution of robot perception technology. When more robots are equipped with vision systems that "surpass the human eye," the digitalization and intellectualization of the physical world will no longer be confined to science fiction but become a tangible, pervasive reality.
References
- https://www.robosense.ai/en/rslidar/AC1
- https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/NPlwN-eF5jpQRRksHeGDfQ?scene=1
Disclaimer: This content is shared with friendly intentions. If any rights are infringed, please notify us promptly, and we will remove it immediately.