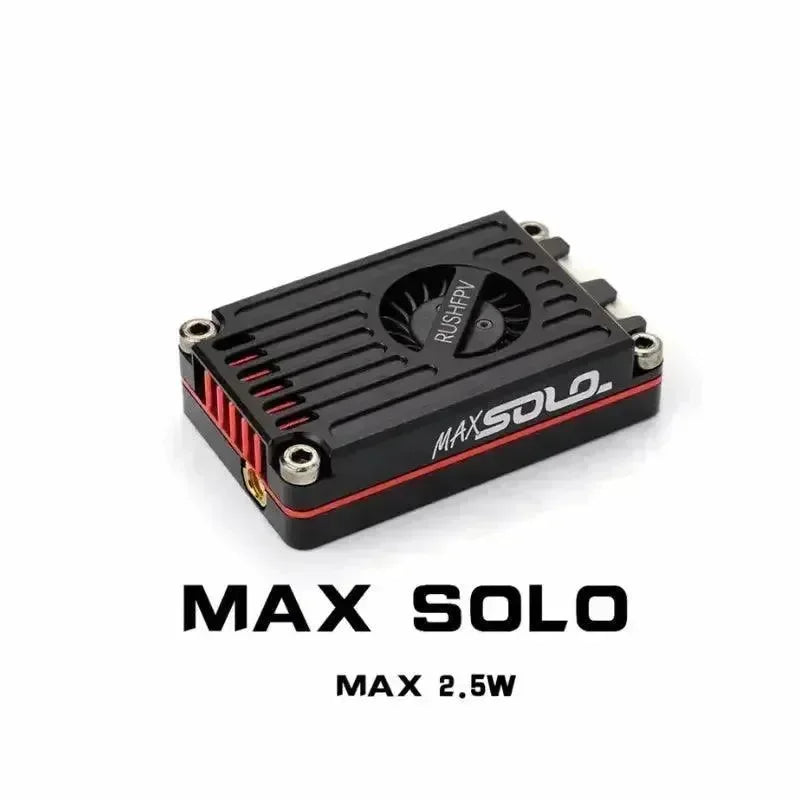
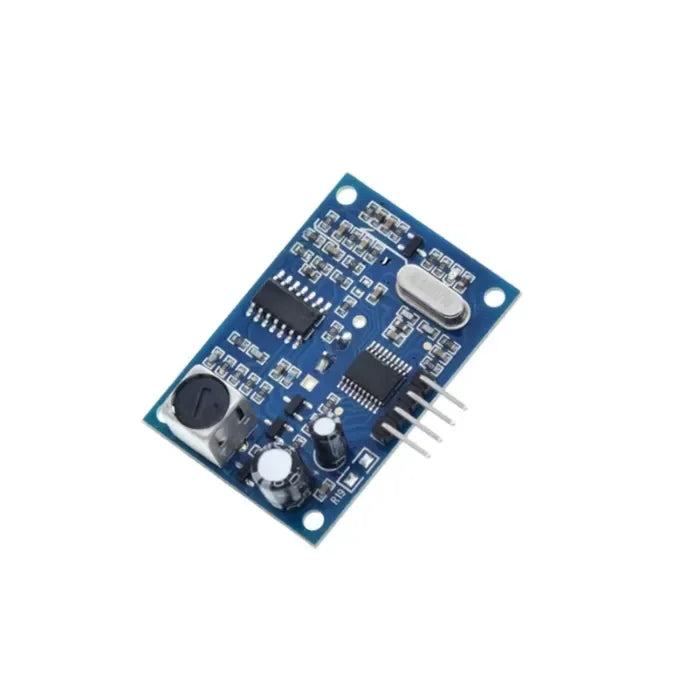
Was ist LILYGO t-embed CC1101?
Das LILYGO T-Embed CC1101 ist ein Entwicklungsboard, das auf der ESP32-Architektur basiert und über integrierte Wi-Fi, Bluetooth Konnektivität, ein OLED-Display, eine USB-C Schnittstelle und mehrere Sensorinterfaces verfügt. Dieses Board dient als robuste Plattform für die Embedded-Entwicklung, insbesondere in den Bereichen Internet der Dinge (IoT), Sensordatenakquise und drahtlose Kommunikation, sowie in anderen Anwendungen von eingebetteten Systemen. Es ist programmierbar mit entweder derArduino Integrierten Entwicklungsumgebung (IDE) oder PlatformIO, was Entwicklern Flexibilität bietet.
Das LILYGO T-Embed CC1101 ist ein leistungsstarkes Embedded-Entwicklungsboard, das besonders für Sub-GHz-Funkkommunikationsanwendungen geeignet ist. Es verfügt über einen integrierten CC1101-Transceiver und eine Funkantenne, die mehrere Frequenzbänder unterstützt (300-348 MHz, 387-464 MHz und 779-928 MHz). Darüber hinaus kann es mit externen Funkmodulen arbeiten, was es ideal für Szenarien macht, die niedrigen Stromverbrauch und lange Reichweite erfordern, wie IoT, drahtlose Sensornetzwerke und Fernsteuersysteme.
Hauptmerkmale des LILYGO T-Embed CC1101:
- Integriertes Sub-GHz-Wireless-Modul:
- Das Board ist mit dem CC1101-Transceiver-Chip ausgestattet, der weithin als ein energieeffizienter Funkfrequenz- (RF) Chip anerkannt ist, der speziell für die drahtlose Kommunikation innerhalb der Frequenzbänder von 300-348 MHz, 387-464 MHz und 779-928 MHz entwickelt wurde. Diese Frequenzbänder werden umfassend für die drahtlose Kommunikation über lange Strecken und mit geringem Energieverbrauch in verschiedenen globalen Regionen genutzt.
- Der CC1101 ist so konzipiert, dass er mehrere Frequenzbänder unterstützt, was seine Vielseitigkeit und Kompatibilität mit verschiedenen globalen drahtlosen Standards gewährleistet.
- Kommunikationsreichweite:
- Die maximale Kommunikationsreichweite des LILYGO T-Embed CC1101 kann unter optimalen Bedingungen bis zu 50 Meter betragen, abhängig von Umweltfaktoren und physischen Hindernissen. Die effektive Reichweite kann in praktischen Anwendungen variieren; jedoch ist das Gerät gut geeignet für eine Vielzahl von Internet of Things (IoT) und drahtlosen Sensoranwendungen, die mittlere Kommunikationsfähigkeiten erfordern.
- Multi-Frequenzunterstützung:
- Diese Frequenzbereiche werden häufig für drahtlose Kommunikation mit niedriger Leistung und großer Reichweite genutzt. Die Bereitstellung mehrerer Frequenzbänder bietet Flexibilität, die von den spezifischen Anforderungen der Region und der Anwendung abhängt.
- Der T-Embed CC1101 unterstützt Sub-GHz Frequenzen in den folgenden Bereichen: 300-348 MHz;387-464 MHz;779-928 MHz.
- Externe Modulunterstützung:
- Neben dem integrierten CC1101-Transceiver ist das T-Embed CC1101 auch mit externen Funkmodulen kompatibel, die die CC1101-Transceiver-Technologie nutzen. Diese Funktionalität ermöglicht es den Benutzern, entweder externe Module oder Antennen zu verwenden, wodurch die Reichweite der drahtlosen Kommunikation erhöht oder die Integration des Geräts in verschiedene drahtlose Ökosysteme erleichtert wird.
- Externe Module haben das Potenzial, den Signalempfang zu verbessern und die Betriebsreichweite zu erweitern, abhängig von der Konfiguration und Platzierung der Antenne.
- Niedrigenergie-Drahtlose Kommunikation:
- Der CC1101-Chip ist für den Betrieb mit geringem Stromverbrauch konzipiert, was ihn ideal für batteriebetriebene Geräte und Anwendungen macht, die eine langanhaltende Leistung mit minimalem Bedarf an Batteriewechsel erfordern.
- Anwendungen:
- Internet der Dinge (IoT) Geräte: Diese Geräte sind besonders gut geeignet für Anwendungen, die eine langstreckige, energieeffiziente Kommunikation erfordern. Beispiele sind intelligente Sensoren, Systeme zur Umweltüberwachung und Technologien zur Hausautomatisierung.
- Drahtlose Sensornetzwerke: Diese Netzwerke werden verwendet, um drahtlose Verbindungen zwischen Sensoren für die Datensammlung in verschiedenen Sektoren herzustellen, einschließlich Landwirtschaft, Umweltüberwachung und industrielle Automatisierung.
- Fernbedienungssysteme: Fernbedienungssysteme spielen eine entscheidende Rolle in verschiedenen Anwendungen, einschließlich Garagentoröffner, Smart Locks und anderen Geräten, die aus der Ferne betrieben werden.
- Smart Cities: Diese Technologien können in verschiedenen Anwendungen im Zusammenhang mit Smart Cities genutzt werden, einschließlich smarter Parklösungen, effizienter Abfallmanagementsysteme und der Überwachung städtischer Infrastrukturen.
Was ist Flipper Zero?
Flipper Zero ist ein Open-Source-Hardware-Tool, das für die Zwecke des Hackens, Steuerens und Emulierens verschiedener drahtloser Signale entwickelt wurde. Es umfasst eine Vielzahl integrierter Funktionen, darunter Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), Infrarot (IR) Fernbedienung, Sub-1 GHz drahtlose Signalübertragung, 1-Wire Kommunikation, iButton-Technologie und Bluetooth Konnektivität. Darüber hinaus ist das Gerät mit integrierten Bildschirmen und Tasten ausgestattet. Flipper Zero ist darauf ausgelegt, als vielseitiges Werkzeug für drahtloses Debugging und Hacking-Anwendungen zu fungieren.

Hauptmerkmale von Flipper Zero:
- Drahtlose Signalinteraktionen:
- Sub-1 GHz-Transceiver: Der Sub-1 GHz-Transceiver ist dafür ausgelegt, mit Geräten zu interagieren, die im Sub-1 GHz-Frequenzbereich arbeiten, einschließlich Garagentoröffner, Fernbedienungen und Schlüsselanhängern. Er verfügt über die Fähigkeit, Signale effektiv zu erfassen, zu analysieren und zu replizieren.
- RFID (Radiofrequenzidentifikation): Das System ist in der Lage, RFID-Tags zu lesen, zu emulieren und Brute-Force-Techniken anzuwenden, insbesondere bei denen, die bei niedriger Frequenz (125 kHz) und hoher Frequenz (13,56 MHz) arbeiten.
- Infrarot (IR) Kommunikation: Funktioniert als universelle Fernbedienung, die in der Lage ist, Infrarotsignale zu lesen und zu übertragen, um Fernseher, Klimaanlagen und verschiedene andere Geräte zu steuern.
- Bluetooth: Diese Technologie ist in der Lage, mit Bluetooth-Geräten zu interagieren sowie Funktionen wie Signal-Sniffing, Emulation und Analyse durchzuführen.
- Vielseitige Hardware-Debugging:
- GPIO (Allzweck-Ein-/Ausgang): Flipper Zero verfügt über die Fähigkeit, mit externen Hardwarekomponenten über seine GPIO-Pins zu interagieren und diese zu steuern. Diese Funktion ermöglicht es den Benutzern, verschiedene elektronische Komponenten zu debuggen und mit ihnen zu interagieren, wodurch die Interaktion mit elektronischen Systemen verbessert wird.
- iButton-Unterstützung: Die Fähigkeit, iButton-Geräte zu lesen und zu emulieren, die als Zugangsschlüssel in physischen Sicherheitssystemen verwendet werden, ist verfügbar.
- NFC (Near-Field Communication): Das Gerät ist in der Lage, NFC-Tags zu lesen und zu emulieren, die in kontaktlosen Zahlungssystemen und Zugangskontrollkarten verwendet werden.
- Eigenständige Funktionalität:
- Der Flipper Zero funktioniert als ein völlig unabhängiges Gerät, das die Notwendigkeit eines Personal Computers oder zusätzlicher Hardware für seine Funktionalität beseitigt. Er ist mit einem LCD-Bildschirm und einer benutzerfreundlichen Tastenoberfläche ausgestattet, die eine einfache Navigation durch seine verschiedenen Werkzeuge und Funktionen ermöglicht.
- Erweiterbar und anpassbar:
- Open Source: Flipper Zero arbeitet mit einer Open-Source-Firmware namens Flipper OS, die es Benutzern ermöglicht, benutzerdefinierte Plugins zu entwickeln und deren Funktionen zu ändern.
- Gemeinschaftsunterstützung: Die Plattform verfügt über eine robuste Gemeinschaft von Entwicklern, die aktiv beitragen, indem sie zusätzliche Werkzeuge, Funktionen und Software erstellen und verbreiten.
- Externe Module: Das System ermöglicht die Integration externer Hardwareerweiterungen, wie sie für Wi-Fi-Penetrationstests verwendet werden, über seine Allgemeinen Eingangs-/Ausgangs (GPIO) Pins oder über spezielle Erweiterungsmodule.
- Tragbar und benutzerfreundlich:
- Kompaktes Design mit einer intuitiven Benutzeroberfläche.
- Integrierter wiederaufladbarer Akku für Tragbarkeit und Feldtests.
Anwendungen von Flipper Zero:
- Sicherheitsforschung:
- Durchführung von Penetrationstests für Drahtlosnetzwerke, Radiofrequenz-Identifikationssysteme (RFID), Near Field Communication (NFC) Geräte und Sub-1 GHz-Signaltechnologien.
- Testen von Schwachstellen in Zugangskontrollsystemen, Fernbedienungen und Kommunikationsprotokollen.
- Drahtlose Signalmanipulation:
- Erfassen, Analysieren und Wiedergeben von RF-Signalen (z. B. um Garagentore zu öffnen, Fernbedienungen zu klonen oder mit anderen RF-Geräten zu interagieren).
- RFID-Tags für Zugangskontrollsysteme emulieren.
- Hardware-Debugging und IoT-Entwicklung:
- Schnittstelle mit externen Elektronikkomponenten zur Fehlersuche oder Prototypenerstellung von IoT-Geräten.
- Debugging und Steuerung von Geräten über GPIO.
- Lehrmittel:
- Nützlich zum Lernen über drahtlose Protokolle, Signalanalysen und Sicherheitssysteme.
- Ideal für Anfänger, die sich für Hardware-Hacking oder die Testung von drahtlosen Signalen interessieren.
LILYGO t-embed VS Flipper Zero
| Besonderheit | LilyGO T-Embed | Flipper Zero |
| Entwicklungsplattform | Basierend auf ESP32, unterstützt Arduino IDE und PlatformIO |
Kommt mit Flipper OS, unterstützt auch community-entwickelte Open-Source-Plugins |
| Drahtlose Kommunikation | Wi-Fi, Bluetooth (erweiterbar) | Sub-1 GHz Funk-signale, Bluetooth, IR, RFID |
| Bildschirm und Benutzeroberfläche | 0,91-Zoll-OLED-Bildschirm, USB-C-Schnittstelle | 1,4-Zoll-LCD-Bildschirm, mehrere physische Tasten, integrierte USB-Schnittstelle |
| Batterie | Stromversorgung über USB-C | Integrierter wiederaufladbarer Akku (ca. 1500mAh) |
| Anwendungsszenarien |
IoT-Entwicklung, Embedded-System-Projekte, Datenaufnahme, Fernsteuersysteme |
Sicherheitsforschung, drahtloses Signalknacken, Penetrationstests, Signalmanipulation und Hacking-Tools |
| Open Source-Unterstützung |
Ja, geeignet für Entwickler, unterstützt die Arduino IDE. und PlatformIO |
Ja, Open-Source, von der Community unterstützt, mit vielen Drittanbieter-Plugins. |
| Benutzeroberfläche | Einfaches OLED-Display (hauptsächlich zur Statusanzeige) |
1,4-Zoll-LCD-Bildschirm mit einem integrierten Menüsystem, unterstützt komplexe Operationen |
| Funktionalität/Erweiterbarkeit |
Hoch, kann durch externe erweitert werden Hardware und Software |
Spezialisierte Funktionalität, unterstützt aber auch Plugins für zusätzliche Funktionen. |
Detaillierter Vergleich der Funktionen (LILYGO t-embed VS flipper zero)
| Besonderheit | LilyGO T-Embed | Flipper Zero |
| Primäre Funktion |
Eingebettete Entwicklungsplattform für IoT, Sensornetzwerke und Fernsteuersysteme |
Drahtloses Signal-Hacking, Penetrationstests, und Sicherheitsforschungswerkzeug |
| Drahtlose Kommunikation |
Unterstützt Wi-Fi und Bluetooth, ideal für vernetzte und drahtlose Kommunikation über kurze Strecken |
Unterstützt Sub-1 GHz, RFID, Infrarot und andere drahtlose Protokolle für Signal-Hacking |
| Anwendungsfall |
IoT-Geräte, Smart-Home-Anwendungen, Datenaufnahme, Fernsteuersysteme |
Drahtloses Signalknacken, RFID-Klonen, Fernbedienungshacking und Penetrationstests |
| Hardware-Erweiterung |
Basierend auf ESP32, unterstützt viele Hardwareperipheriegeräte. und Erweiterungsmodule für flexible Designs |
Begrenzte Expansion, konzentriert auf die Analyse und Steuerung von drahtlosen Signalen; unterstützt externe Module für einige Funktionen |
| Entwicklungsumgebung |
Unterstützt Arduino IDE und PlatformIO für schnelles Prototyping und Entwicklung |
Vorkonfiguriertes Betriebssystem (Flipper OS), Open Source, unterstützt Drittanbieter-Plugins und von der Community entwickelte Funktionen |
| Besondere Merkmale |
Niedrigenergie, langreichweitige Kommunikation mit CC1101-Transceiver, ideal für IoT, Sensornetzwerke |
RFID, iButton-Unterstützung, Emulation und Knacken von Zugangskarten für Türen, Garagentoröffner, Autoschlüssel usw. |
| Sicherheits-/Cracking-Fokus |
Nicht speziell für Sicherheit oder Knacken entwickelt, mehr auf drahtlose Kommunikation und IoT fokussiert |
Entwickelt für Sicherheitsforschung, Signalentschlüsselung, und Penetrationstests (z. B. RFID, IR, Sub-1 GHz-Protokolle) |
| Benutzeroberfläche | Einfaches OLED-Display, grundlegende Schnittstelle für Informationsanzeige und Debugging |
LCD-Bildschirm mit Tasten, menügesteuerte Benutzeroberfläche zum Testen und Steuern verschiedener drahtloser Protokolle |
| Hauptpublikum | Ingenieure, Entwickler, die an eingebettete Systeme und IoT-Projekte |
Hacker, Sicherheitsforscher, Enthusiasten für drahtlose Signale, und Penetrationstester |
| Anpassung | Hochgradig anpassbar mit externen Hardware- und Softwareentwicklung |
Anpassbar mit Drittanbieter-Plugins, beschränkt auf die Manipulation von Funksignalen |
| Batterie | Über USB-C betrieben, kann sein mit externen Batterien verwendet |
Wiederaufladbare Batterie, entworfen für tragbare Hacking-Sitzungen |
| Kompatibilität | Primär für IoT, Fernsteuerung, entworfen und Datenanwendungsprogramme |
Kompatibel mit verschiedenen drahtlosen Protokollen, Fernbedienungen, RFID-Systeme und mehr |
Zusammenfassung der wichtigsten Unterschiede
-
Das LilyGO T-Embed ist der eingebetteten Entwicklung gewidmet, mit einem besonderen Schwerpunkt auf dem Internet der Dinge (IoT) und sensorbasierten Anwendungen. Diese Plattform bietet eine vielseitige Umgebung, die eine breite Palette von Hardware unterstützt, Wi-Fi- und Bluetooth-Funktionen integriert und eine benutzerfreundliche Entwicklungserfahrung durch die Arduino Integrated Development Environment (IDE) und PlatformIO bietet.
-
Flipper Zero ist ein spezialisiertes Werkzeug, das für die Manipulation von drahtlosen Signalen entwickelt wurde, einschließlich des Hackens und der Emulation von RFID, Sub-1 GHz-Signalen und Infrarotsignalen. Dieses Gerät ist für den Einsatz in der Sicherheitsforschung, Penetrationstests und verschiedenen Hacking-Aktivitäten gedacht. Es verfügt über eine benutzerfreundliche Oberfläche und betont robuste Signalanalysen und Steuerungsfähigkeiten.
FAQs
Wie unterscheidet sich Flipper Zero?
- All-in-One-Gerät: Im Gegensatz zu spezialisierten Hacking-Tools kombiniert der Flipper Zero mehrere Funktionen (RF, NFC, Bluetooth, IR, GPIO) in einem einzigen tragbaren Gerät.
- Rechtlich und Sicher: Entwickelt für rechtliche Sicherheitsforschung und Bildungszwecke, fördert es verantwortungsbewusstes Hacken und das Lernen über drahtlose Systeme.
- Benutzerfreundliche Oberfläche: Einfach für Anfänger zu bedienen und dennoch leistungsstark genug für fortgeschrittene Benutzer.
- Tragbar und batteriebetrieben: Das kompakte, eigenständige Design ermöglicht Feldarbeit, ohne zusätzliche Hardware oder Stromquellen zu benötigen.
Was Flipper Zero NICHT ist:
- Standardmäßig kein Wi-Fi-Hacking-Gerät: Im Gegensatz zu anderen Werkzeugen (z. B. Pineapple) verfügt Flipper Zero nicht von Haus aus über Wi-Fi-Hacking-Funktionen. Diese Funktionalität kann jedoch mit externen Modulen hinzugefügt werden.
- Kein Spielzeug: Trotz seines freundlichen und lustigen Designs (mit einem virtuellen Delfin-Maskottchen) ist Flipper Zero ein ernsthaftes Werkzeug für Fachleute und Enthusiasten.
Warum Sub-GHz-Kommunikation wählen (z.B. CC1101)?
- Niedriger Stromverbrauch:
- Sub-GHz-Drahtloskommunikation ist bekannt für ihren geringen Stromverbrauch, was sie ideal für Geräte macht, die lange Zeit mit Batteriestrom betrieben werden müssen. Der CC1101-Chip ist auf Energieeffizienz optimiert, was eine verlängerte Batterielebensdauer in IoT- und Sensortechnologien ermöglicht.
- Langstreckenkommunikation:
- Sub-GHz-Frequenzen, wie 433 MHz, 868 MHz und 915 MHz, bieten längere Kommunikationsreichweiten im Vergleich zu 2,4 GHz-Kommunikation. Die Signale mit niedrigerer Frequenz haben bessere Ausbreitungseigenschaften, was bedeutet, dass sie weiter reisen und Hindernisse (wie Wände) effektiver durchdringen können.
- Reduzierte Interferenz:
- Sub-GHz-Bänder sind weniger überfüllt als das 2,4-GHz-Band, das von vielen Geräten wie Wi-Fi, Bluetooth und Mikrowellen genutzt wird. Dies verringert das Risiko von Interferenzen und sorgt für eine zuverlässigere Kommunikation, insbesondere in Umgebungen mit vielen drahtlosen Geräten.